MobileNet V3¶
Introduction¶
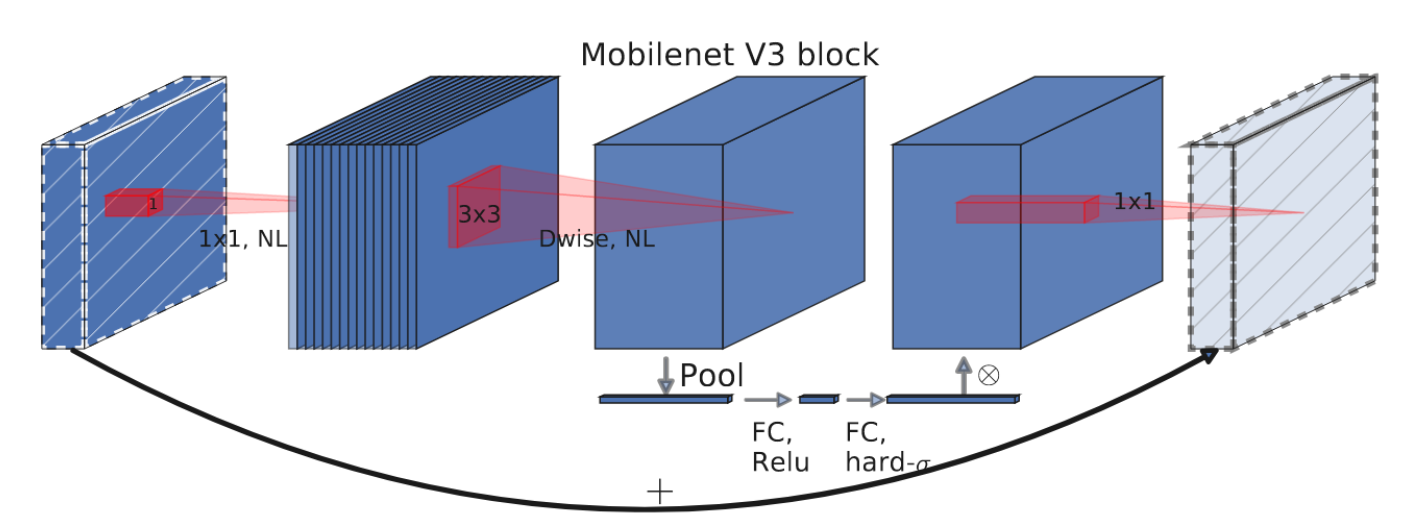
MobileNet V3 is initially described in the paper. MobileNetV3 parameters are obtained by NAS (network architecture search) search, and some practical results of V1 and V2 are inherited, and the attention mechanism of SE channel is attracted, which can be considered as a masterpiece. The author create two new MobileNet models for release: MobileNetV3-Large and MobileNetV3-Small which are targeted for high and low resource use cases. These models are then adapted and applied to the tasks of object detection and semantic segmentation. The author of MobileNet V3 measure its performance on Imagenet classification, COCO object detection, and Cityscapes segmentation.
Abstract¶
Show the paper's abstract
We present the next generation of MobileNets based on a combination of complementary search techniques as well as a novel architecture design. MobileNetV3 is tuned to mobile phone CPUs through a combination of hardware-aware network architecture search (NAS) complemented by the NetAdapt algorithm and then subsequently improved through novel architecture advances. This paper starts the exploration of how automated search algorithms and network design can work together to harness complementary approaches improving the overall state of the art. Through this process we create two new MobileNet models for release: MobileNetV3-Large and MobileNetV3-Small which are targeted for high and low resource use cases. These models are then adapted and applied to the tasks of object detection and semantic segmentation. For the task of semantic segmentation (or any dense pixel prediction), we propose a new efficient segmentation decoder Lite Reduced Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (LR-ASPP). We achieve new state of the art results for mobile classification, detection and segmentation. MobileNetV3-Large is 3.2% more accurate on ImageNet classification while reducing latency by 15% compared to MobileNetV2. MobileNetV3-Small is 4.6% more accurate while reducing latency by 5% compared to MobileNetV2. MobileNetV3-Large detection is 25% faster at roughly the same accuracy as MobileNetV2 on COCO detection. MobileNetV3-Large LR-ASPP is 30% faster than MobileNetV2 R-ASPP at similar accuracy for Cityscapes segmentation.
How to use it?¶
from mmpretrain import inference_model
predict = inference_model('mobilenet-v3-small-050_3rdparty_in1k', 'demo/bird.JPEG')
print(predict['pred_class'])
print(predict['pred_score'])
import torch
from mmpretrain import get_model
model = get_model('mobilenet-v3-small-050_3rdparty_in1k', pretrained=True)
inputs = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
out = model(inputs)
print(type(out))
# To extract features.
feats = model.extract_feat(inputs)
print(type(feats))
Prepare your dataset according to the docs.
Train:
python tools/train.py configs/mobilenet_v3/mobilenet-v3-small_8xb128_in1k.py
Test:
python tools/test.py configs/mobilenet_v3/mobilenet-v3-small-050_8xb128_in1k.py https://download.openmmlab.com/mmclassification/v0/mobilenet_v3/mobilenet-v3-small-050_3rdparty_in1k_20221114-e0b86be1.pth
Models and results¶
Image Classification on ImageNet-1k¶
Model |
Pretrain |
Params (M) |
Flops (G) |
Top-1 (%) |
Top-5 (%) |
Config |
Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
From scratch |
1.59 |
0.02 |
57.91 |
80.19 |
||
|
From scratch |
2.04 |
0.04 |
65.23 |
85.44 |
||
|
From scratch |
2.54 |
0.06 |
66.68 |
86.74 |
||
|
From scratch |
2.54 |
0.06 |
67.66 |
87.41 |
||
|
From scratch |
5.48 |
0.23 |
73.49 |
91.31 |
||
|
From scratch |
5.48 |
0.23 |
74.04 |
91.34 |
Models with * are converted from the official repo. The config files of these models are only for inference. We haven’t reproduce the training results.
Citation¶
@inproceedings{Howard_2019_ICCV,
author = {Howard, Andrew and Sandler, Mark and Chu, Grace and Chen, Liang-Chieh and Chen, Bo and Tan, Mingxing and Wang, Weijun and Zhu, Yukun and Pang, Ruoming and Vasudevan, Vijay and Le, Quoc V. and Adam, Hartwig},
title = {Searching for MobileNetV3},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
month = {October},
year = {2019}
}